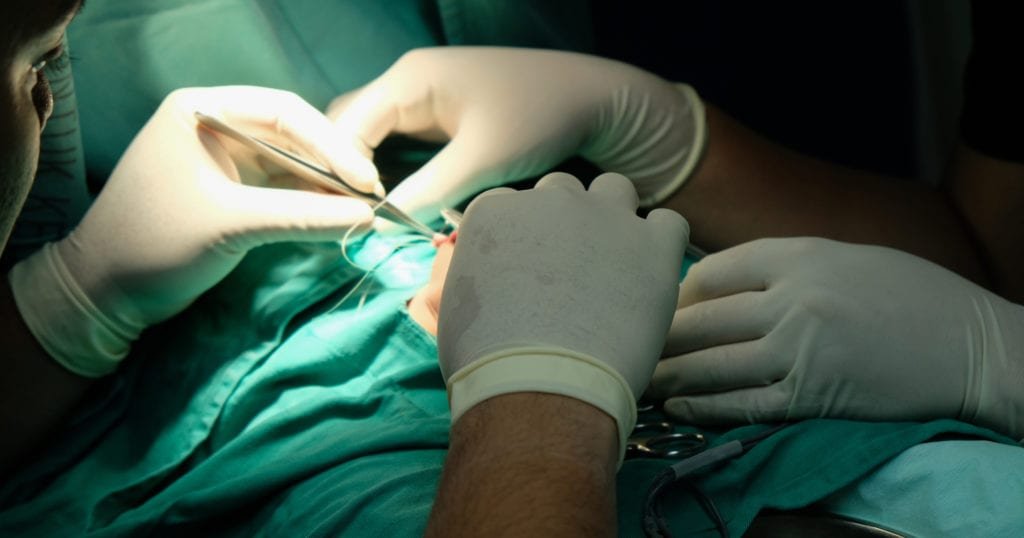
Minor skin surgery plays a crucial role in dermatology and general healthcare, offering effective solutions for a range of skin conditions that require surgical intervention but do not necessitate general anesthesia or hospital admission. These procedures are typically quick, minimally invasive, and performed under local anesthesia. Whether you are dealing with a suspicious mole, a bothersome skin tag, or a cyst, minor skin surgery provides a reliable pathway to diagnosis, treatment, and recovery.
In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about minor skin surgery—from types of procedures and common conditions treated to preparation, recovery, and benefits. Whether for health or cosmetic reasons, understanding your options can help you make informed decisions with confidence.
What Is Minor Skin Surgery?
Minor skin surgery refers to surgical procedures performed on the skin or just beneath it, often in an outpatient setting. These surgeries are typically performed using local anesthesia, meaning the patient remains awake but the area being treated is numbed. The procedures are often short in duration and carry a low risk of complications.
The main goals of minor skin surgery include:
- Removing abnormal skin growths such as moles, warts, skin tags, or cysts
- Diagnosing suspicious lesions through biopsy
- Treating skin cancers such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma in their early stages
- Improving cosmetic appearance by removing benign but unsightly growths
Minor skin surgeries are usually performed by dermatologists, general practitioners with special training, or surgeons in clinics or medical centers.
Common Conditions Treated with Minor Skin Surgery
Minor skin surgery is often the best course of treatment for several skin conditions. Here are some of the most frequently treated issues:
1. Moles (Nevi)
Moles are common skin growths that are usually harmless. However, if a mole changes in size, shape, or color, or becomes symptomatic, it may need to be surgically removed and sent for histopathological examination to rule out melanoma.
2. Skin Tags
These are small, soft, benign skin growths that often appear in areas of friction such as the neck, armpits, and groin. While harmless, they can be removed for comfort or cosmetic reasons using techniques like excision, cryotherapy, or cauterization.
3. Warts
Caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), warts are contagious and may require surgical removal if resistant to topical treatments. Curettage, electrosurgery, and laser treatments are effective methods.
4. Sebaceous Cysts
Cysts are sac-like pockets filled with fluid or semi-solid material. If infected or causing discomfort, they can be excised completely to prevent recurrence.
5. Lipomas
These are noncancerous fatty tumors that grow slowly under the skin. Surgical excision is typically performed if the lipoma becomes painful or increases in size.
6. Skin Cancers
Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma often require prompt surgical removal. Early-stage skin cancers can be effectively treated with minor surgery such as excision or Mohs micrographic surgery.
Types of Minor Skin Surgery Procedures
Minor skin surgery includes various procedures, each tailored to the specific condition and the location of the lesion.
Excision Surgery
This involves cutting out the lesion along with a small margin of normal tissue. The wound is then closed with stitches. It’s commonly used for moles, cysts, and skin cancers.
Shave Excision
The growth is shaved off with a scalpel, typically used for raised lesions that do not require deep excision.
Punch Biopsy
A circular blade is used to remove a small core of skin. This is usually done to diagnose skin diseases or evaluate moles.
Cryotherapy
Liquid nitrogen is applied to freeze and destroy abnormal tissue. It’s ideal for treating warts, actinic keratoses, and some benign growths.
Electrosurgery (Cauterization)
Electric current is used to cut tissue or stop bleeding. This method is effective for removing small growths like skin tags and warts.
Curettage and Desiccation
The lesion is scraped off with a curette, and the area is treated with electrical current to stop bleeding and kill remaining cells.
What to Expect Before, During, and After the Procedure
Before the Procedure
Your healthcare provider will evaluate the lesion and determine the best surgical approach. You may be asked about:
- Your medical history and current medications
- Any allergies, especially to anesthetics
- Any bleeding disorders or use of blood thinners
You may also be advised to avoid alcohol and certain medications a few days before surgery to minimize bleeding risk.
During the Procedure
- The area is cleaned and numbed with a local anesthetic.
- The procedure itself typically lasts 15 to 45 minutes, depending on the complexity.
- Most patients experience minimal discomfort and can watch or look away as preferred.
After the Procedure
- The surgical site is cleaned, bandaged, and you will receive aftercare instructions.
- Pain is usually mild and can be managed with over-the-counter medication.
- Stitches, if used, are removed after 5–14 days depending on the site.
- You’ll be advised on how to keep the area clean and when to return for a follow-up.
Risks and Complications
Minor skin surgery is considered safe, but like all medical procedures, it carries some risks:
- Infection: Usually preventable with proper wound care
- Bleeding or bruising: Minimal and typically resolves quickly
- Scarring: Varies based on the procedure and individual healing ability
- Recurrence: Some lesions like cysts can return if not completely removed
- Allergic reactions: Rare, but possible with anesthetics or antiseptics
By following post-operative instructions and choosing a qualified practitioner, the risk of complications can be minimized.
Benefits of Minor Skin Surgery
Minor skin surgery offers several advantages over more invasive procedures:
- Minimally invasive with quick recovery
- Performed under local anesthesia, avoiding the risks of general anesthesia
- Cost-effective and often covered by health insurance when medically necessary
- Quick diagnosis through tissue biopsy
- Improved appearance and comfort when removing benign lesions
These benefits make minor skin surgery a highly preferred method for managing both medical and cosmetic skin concerns.
How to Choose the Right Clinic or Surgeon
Choosing the right practitioner is essential to ensure safety and satisfactory outcomes. Here are some tips:
- Look for experience and qualifications in dermatology or minor surgery
- Check reviews and testimonials from previous patients
- Ensure proper hygiene and medical standards in the clinic
- Ask about pricing, aftercare, and support available post-procedure
It’s also important to feel comfortable and well-informed during your consultation. A good provider will answer all your questions and set realistic expectations.
Conclusion
Minor Skin Surgery is a safe, effective, and accessible solution for diagnosing and treating a wide variety of skin conditions. From small benign growths to early skin cancers, these procedures offer minimal discomfort, fast recovery, and lasting results. Whether you are pursuing treatment for medical or cosmetic reasons, consulting a qualified healthcare professional is the first step toward healthier, clearer skin.
By understanding the available procedures, knowing what to expect, and following proper aftercare, you can confidently navigate your skin surgery journey and enjoy the benefits of modern dermatological care.









Leave a Reply