When it comes to mixing solutions in the lab, choosing the right equipment can make all the difference. Let’s dive into the world of lab mixers and see how orbital shakers stack up against other options.
Understanding Lab Mixers
Lab mixers are essential tools in scientific research, ensuring that samples are thoroughly combined. They come in various types, each designed for specific applications.
Types of Lab Mixers
- Orbital Shakers: These devices move samples in a circular motion, ideal for culturing cells and mixing solutions gently.
- Vortex Mixers: Designed for rapid mixing of small volumes, they create a vortex to quickly blend contents.
- Rockers: Provide a gentle rocking motion, suitable for delicate samples like gels and blots.
- Rotators: Rotate samples end-over-end, perfect for mixing blood samples or other suspensions.
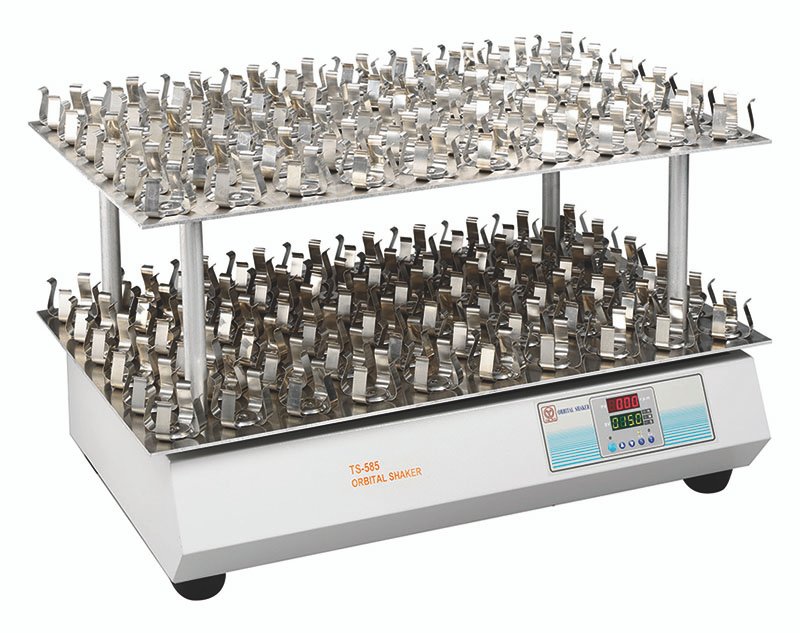
Deep Dive into Orbital Shakers
Orbital shakers are a staple in many laboratories. They operate by moving samples in a circular motion, which ensures even mixing without introducing bubbles. This makes them ideal for applications like cell culture, where gentle agitation is crucial.
Advantages of Orbital Shakers
- Versatility: Suitable for various container types, including flasks, bottles, and tubes.
- Consistency: Provides uniform mixing, essential for reproducible results.
- Temperature Control: Many models come with built-in temperature settings, allowing for precise incubation conditions.
Limitations of Orbital Shakers
- Space Requirements: They can occupy significant bench space.
- Not Ideal for High-Speed Mixing: For tasks requiring rapid agitation, other mixers might be more suitable.
Comparing Orbital Shakers to Other Mixers
Orbital Shakers vs. Vortex Mixers
While both are used for mixing, their applications differ. Vortex mixers are best for quickly mixing small volumes, whereas orbital shakers handle larger volumes and provide gentler mixing.
Orbital Shakers vs. Rockers
Rockers offer a tilting motion, making them ideal for gel staining. In contrast, orbital shaker provide a more vigorous mixing action, suitable for cell cultures.
Orbital Shakers vs. Rotators
Rotators mix samples by rotating them end-over-end, which is excellent for keeping particles in suspension. Orbital shakers, however, are better for applications requiring continuous agitation.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Mixer
- Sample Volume: Determine the typical volume you’ll be mixing.
- Mixing Speed: Some applications require rapid mixing, while others need gentle agitation.
- Temperature Sensitivity: If your samples are temperature-sensitive, look for mixers with temperature control.
- Available Space: Ensure the equipment fits comfortably in your lab space.
Applications Best Suited for Orbital Shakers
- Cell Culture: Provides the gentle mixing necessary for cell growth.
- Solubility Studies: Helps in dissolving compounds evenly.
- Extraction Procedures: Facilitates the mixing of solvents and samples.
Maintenance Tips for Orbital Shakers
- Regular Cleaning: Keep the platform and exterior clean to prevent contamination.
- Routine Calibration: Ensure the shaker operates at the correct speed and temperature settings.
- Check for Wear and Tear: Regularly inspect belts and other moving parts for signs of wear.
Safety Considerations
- Secure Containers: Always ensure that containers are properly secured to prevent spills.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the shaker’s weight capacity.
- Use Appropriate Containers: Ensure that the containers used are compatible with the shaker’s motion.
Choosing the Right Mixer for Your Laboratory
Selecting the appropriate mixing equipment depends on several factors, including the nature of your samples, the required mixing speed and duration, and the specific applications you intend to perform.
- Sample Volume and Container Type: For mixing larger volumes or using various container types such as flasks, bottles, or test tubes, an orbital shaker is advantageous due to its adjustable platform and gentle mixing action.
- Mixing Speed and Intensity: If rapid mixing of small volumes is necessary, a vortex mixer is appropriate. For applications requiring gentle mixing, such as staining or destaining gels, a rocker or a low-speed orbital shaker may be more suitable.
- Temperature Control: For experiments that require specific temperature conditions, consider using an incubator shaker, which combines the mixing capabilities of an orbital shaker with precise temperature control.
- Application Specificity: For tasks like washing blots or gentle mixing, a rocker provides the necessary motion without causing damage to delicate samples. Conversely, for more vigorous mixing needs, an orbital shaker or vortex mixer may be more appropriate.
Conclusion
Choosing the right lab mixer depends on your specific applications. Orbital shaker offer versatility and gentle mixing, making them suitable for a range of tasks. However, it’s essential to assess your lab’s needs to select the most appropriate equipment.
FAQs
- Can I use an orbital shaker for all mixing tasks?
While versatile, orbital shakers are best for gentle mixing. For rapid or vigorous mixing, other mixers might be more appropriate. - How do I maintain my orbital shaker?
Regular cleaning, routine calibration, and inspecting for wear and tear are essential maintenance steps. - Are orbital shakers suitable for temperature-sensitive samples?
Many orbital shakers come with temperature control features, making them suitable for such applications. - What’s the difference between an orbital shaker and a rocker?
Orbital shakers move samples in a circular motion, while rockers provide a gentle tilting motion.









Leave a Reply