Acoustics play a critical role in the performance of audio visual systems. Whether designing a conference room, auditorium, theater, or hybrid meeting space, achieving clear speech intelligibility, balanced sound coverage, and minimal echo is essential. Poor acoustic design can render even the most advanced AV equipment ineffective. Computer-Aided Design, or CAD, tools have become indispensable in AV projects for acoustic modeling. By integrating acoustic analysis with spatial design, CAD tools enable AV professionals to predict sound behavior, optimize speaker placement, and ensure a high-quality auditory experience.
Understanding Acoustic Modeling in AV Design
Acoustic modeling is the process of simulating how sound propagates within a space. It involves evaluating parameters such as reverberation time, sound pressure levels, frequency response, and coverage patterns. The goal is to identify potential issues, such as dead zones, echo, or excessive reflections, before installation. Accurate acoustic modeling ensures that AV systems deliver consistent audio performance for all participants, whether in-person or remote.
Role of CAD Tools in Acoustic Modeling
CAD tools facilitate acoustic modeling by providing a digital representation of the space and enabling precise placement of speakers, microphones, acoustic panels, and other sound-affecting elements. Designers can simulate various scenarios and evaluate the impact of room dimensions, materials, and equipment configuration on sound quality. CAD software allows AV professionals to experiment with layouts, optimize performance, and minimize costly on-site adjustments.
1. Creating Accurate Room Models
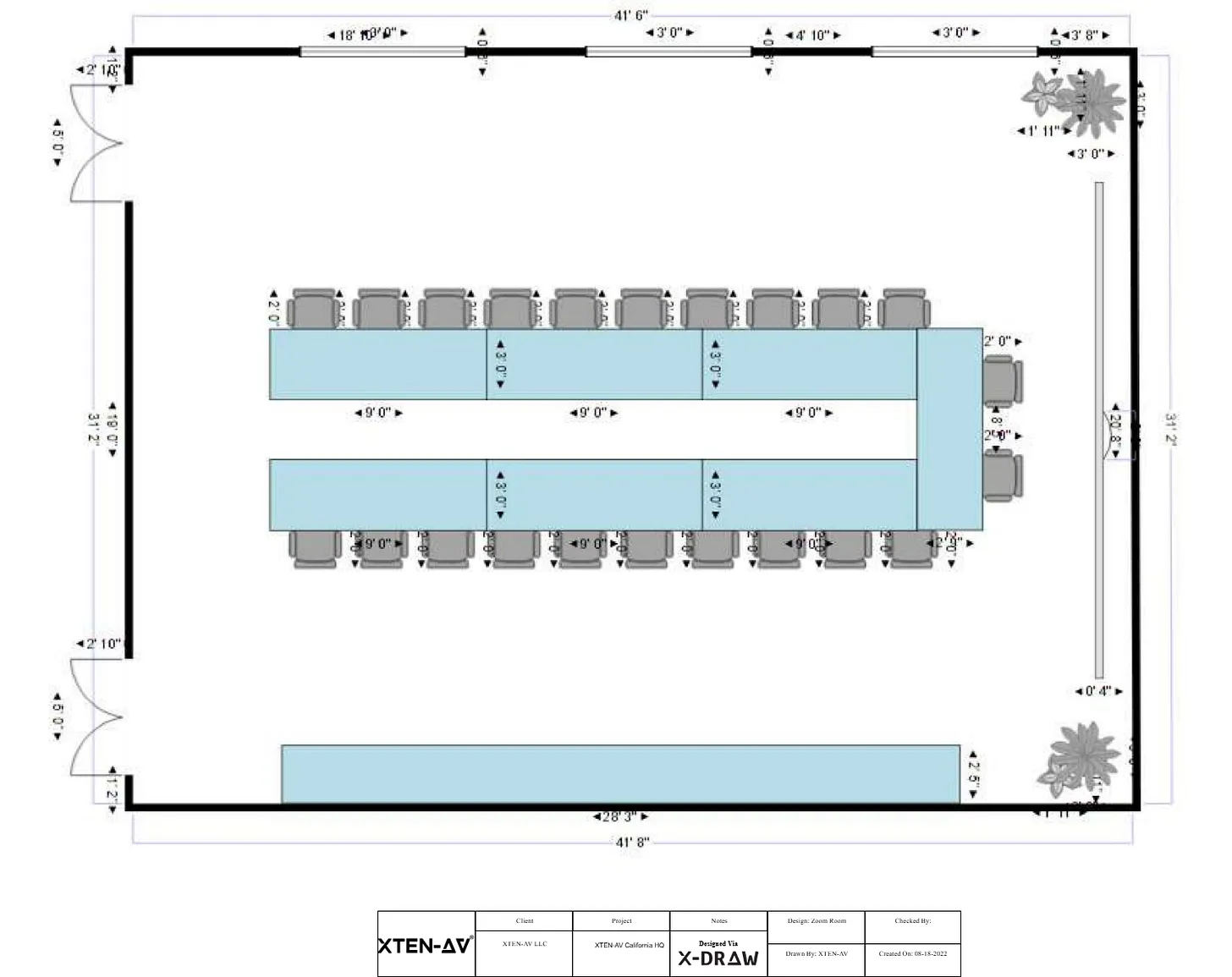
The first step in acoustic modeling is creating an accurate CAD model of the room. This includes walls, ceilings, floors, doors, windows, and fixed furniture. Dimensions, materials, and surface properties must be included because they influence sound reflection, absorption, and diffusion. Accurate room models allow designers to simulate realistic acoustic behavior and make informed decisions regarding speaker placement and acoustic treatment.
2. Material Properties and Acoustic Treatment
Different materials have varying absorption and reflection characteristics. CAD tools allow designers to assign material properties to surfaces, such as gypsum, wood, glass, or carpeting. Acoustic panels, diffusers, and ceiling treatments can also be modeled to evaluate their effect on reverberation and sound clarity. By adjusting materials virtually, designers can optimize room acoustics before physical installation, reducing trial-and-error on-site.
3. Speaker Placement and Coverage Simulation
One of the most critical aspects of acoustic modeling is speaker placement. CAD software enables designers to simulate speaker coverage, sound pressure levels, and polar patterns within the room. By visualizing coverage maps, designers can identify gaps, overlaps, or areas with excessive volume. This ensures even sound distribution and improves speech intelligibility for all participants.
4. Microphone Placement and Feedback Prevention
In addition to speakers, microphones must be strategically positioned to capture sound without causing feedback or interference. CAD tools allow designers to simulate microphone pickup patterns and their interaction with speakers. This helps prevent feedback loops, ensures clear audio capture, and reduces background noise. Virtual testing of microphone configurations saves time and minimizes on-site adjustments.
5. Evaluating Reverberation Time
Reverberation time, or RT60, is a key parameter in acoustic design. It measures how long it takes for sound to decay by 60 decibels in a room. Excessive reverberation can cause speech to become unintelligible, while too little can make the sound feel dry and unnatural. CAD tools calculate RT60 based on room dimensions, materials, and speaker placement. Designers can adjust acoustic treatments or equipment layout to achieve optimal reverberation times for the intended use of the space.
6. Frequency Response Analysis
Different spaces affect low, mid, and high frequencies differently. CAD-based acoustic modeling allows designers to analyze frequency response across the room. Identifying frequency imbalances enables adjustments to speaker types, equalization settings, or acoustic treatments. This ensures consistent audio quality for music, speech, or multimedia content.
7. Integration with 3D Visualization
3D modeling in CAD provides a realistic view of the room and equipment placement. Designers can visualize how sound interacts with surfaces, ceilings, and furniture. 3D visualization also helps communicate design decisions to clients and stakeholders, allowing them to understand acoustic solutions and approve layouts before installation.
8. Scenario Testing and Optimization
CAD tools allow AV designers to test multiple scenarios, such as full occupancy, partial seating, or different speaker configurations. Simulating these scenarios helps optimize system performance under varying conditions. Designers can make adjustments to speaker angles, microphone positions, or acoustic treatments to achieve consistent results.
9. Collaboration with Other Trades
Acoustic modeling often requires coordination with architects, interior designers, and construction teams. CAD tools facilitate collaboration by providing accurate room models that reflect architectural elements. This ensures that acoustic treatments, speaker mounts, and cabling routes are compatible with structural and design requirements.
10. Documentation for QA QC and Installation
Detailed CAD-based acoustic models serve as documentation for quality assurance and quality control. Installers can reference speaker locations, microphone positions, and acoustic treatments directly from the CAD drawings. Proper documentation reduces installation errors and ensures that the system performs as modeled during testing and commissioning.
11. Future-Proofing Acoustic Design
CAD-based acoustic modeling allows designers to plan for future upgrades or expansions. By including extra capacity for speakers, microphones, and acoustic treatments in the CAD model, AV systems can adapt to changing requirements without major redesigns. This future-proofing reduces long-term costs and ensures sustained system performance.
12. Real-Time Adjustments During Design
Modern CAD tools offer real-time feedback, enabling designers to adjust layouts and see immediate impacts on acoustic performance. This iterative process allows for rapid optimization and minimizes the need for physical testing. Real-time adjustments save time and enhance design accuracy.
13. Cost and Time Efficiency
By identifying acoustic issues during the design phase, CAD tools reduce the need for on-site modifications, rework, or additional materials. Simulation and modeling reduce trial-and-error, saving both time and budget. Efficient acoustic modeling ensures that installations are completed on schedule and meet client expectations. techners
14. Client Communication and Visualization
Acoustic performance is often difficult for clients to visualize. CAD tools, combined with 3D rendering and simulation, allow designers to present acoustic maps, speaker coverage, and reverberation effects. This visual representation enhances client understanding, facilitates approvals, and ensures alignment between design intent and expectations.
15. Integration with Overall AV System Design
Acoustic modeling in CAD does not occur in isolation. It integrates with other aspects of AV system design, including video display placement, control systems, and network infrastructure. This holistic approach ensures that audio, video, and control components work together seamlessly, providing a consistent and high-quality user experience.
Conclusion
Acoustic modeling is a fundamental aspect of AV system design, and CAD tools have become essential for achieving accurate, efficient, and scalable solutions. By creating precise room models, simulating speaker and microphone placement, analyzing reverberation and frequency response, and incorporating acoustic treatments, AV designers can predict performance, optimize layouts, and prevent costly on-site issues. CAD tools facilitate collaboration with architects and stakeholders, provide detailed documentation for installation and QA QC, and allow for future-proofing and scenario testing. Leveraging CAD software for acoustic modeling ensures that AV projects deliver clear, balanced, and reliable sound, enhancing the overall user experience and maintaining high standards of quality in both design and installation.
Read more: https://kinkedpress.com/which-cad-tools-are-best-for-multi-room-av-system-design/












Leave a Reply