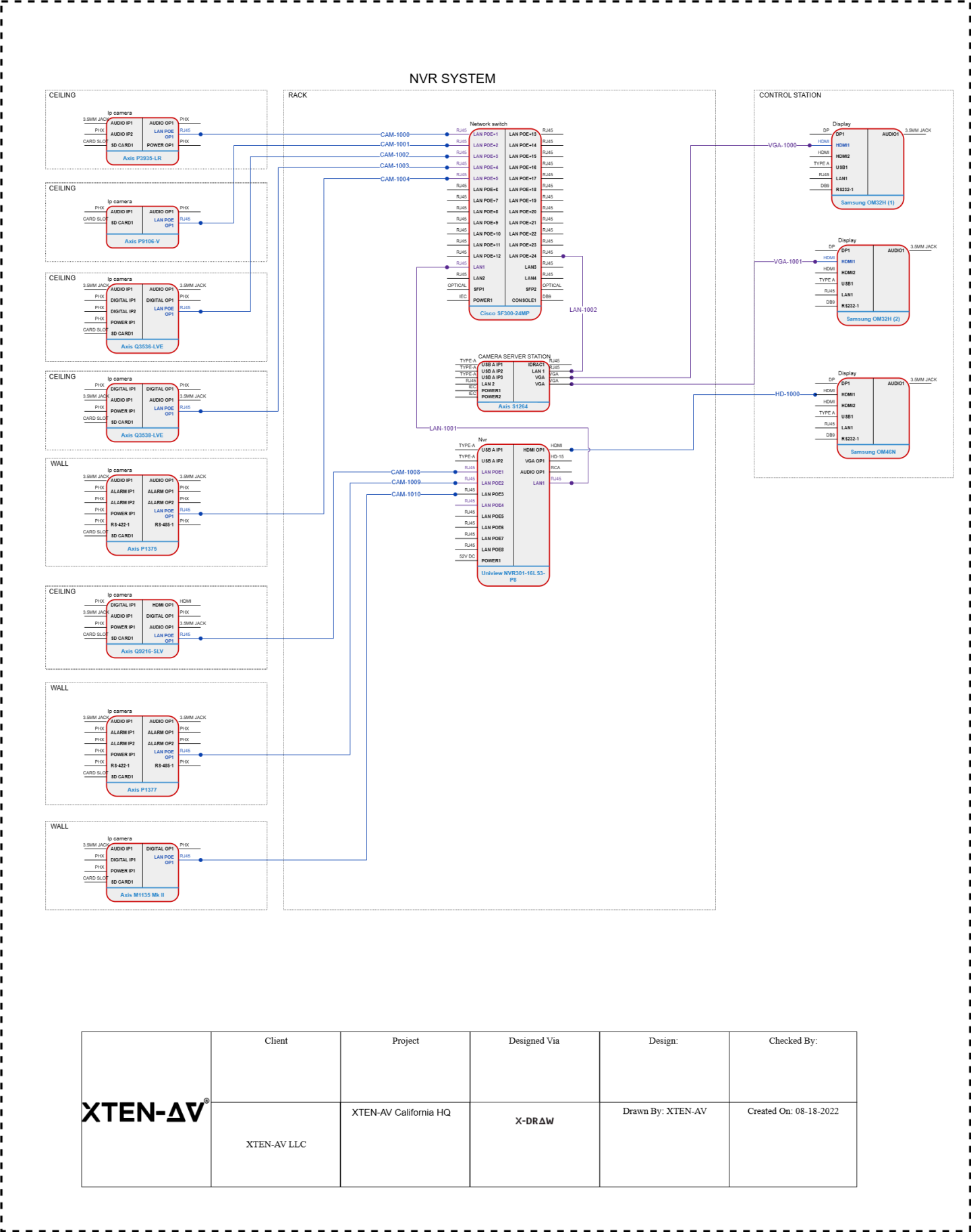
Multi floor building surveillance requires careful planning and implementation to ensure all areas are monitored effectively while maintaining performance, reliability, and security. Network Video Recorders NVRs serve as the central hub for collecting, storing, and managing video feeds from multiple cameras distributed across floors. Setting up an NVR for such environments involves considerations for camera placement, network infrastructure, storage, power, and remote access. This guide provides a comprehensive approach for installing NVR systems in multi floor buildings, suitable for commercial offices, residential complexes, retail malls, and industrial facilities in 2025.
Planning and Design
Effective NVR setup begins with detailed planning. Conduct a site survey to identify critical areas requiring surveillance such as entrances, hallways, staircases, elevators, parking areas, and communal spaces. Determine the number of cameras, their type, resolution, and field of view. For multi floor buildings, consider overlapping coverage to eliminate blind spots. Planning should also account for lighting conditions, camera height, and potential obstructions. Preparing a layout diagram with camera positions simplifies installation and ensures consistent coverage.
Choosing the Right NVR
Multi floor installations often require enterprise grade NVRs capable of handling multiple channels and high resolution streams. Factors to consider include:
- Number of channels: Ensure the NVR can support all cameras with room for future expansion
- Processing power: High resolution cameras and AI analytics require powerful CPUs or dedicated AI processors
- Storage capacity: Adequate storage for continuous recording and retention periods, often with RAID support
- Network interfaces: Multiple LAN ports or support for VLANs to segregate camera traffic
- Remote access: Capability for multiple simultaneous remote users
Selecting an NVR that meets current needs while allowing scalability is essential for long term performance and cost efficiency.
Network Infrastructure
A robust network is critical for multi floor surveillance. IP cameras connect to the NVR via LAN or PoE switches. Key considerations include:
- Structured cabling: Use CAT6 or higher to support high bandwidth and PoE delivery
- PoE switches: Centralize power and data transmission for cameras, reducing cable clutter
- VLANs: Segment the surveillance network from general IT traffic to prevent congestion
- Bandwidth planning: Calculate the total required bandwidth considering camera resolution, frame rate, and compression
- Redundancy: Implement backup links or secondary switches to ensure uninterrupted connectivity
Proper network design ensures stable video streams and reliable performance, even during peak building activity.
Camera Installation
Mount cameras strategically on each floor to maximize coverage. Use corner and ceiling mounts for wide angles, while focusing on entrances, lobbies, and high traffic areas. Multi floor buildings may require stairwell and elevator monitoring, which benefits from cameras with PTZ pan tilt zoom functionality for flexible monitoring. Ensure cameras are securely mounted and properly powered via PoE or dedicated supplies. Adjust camera angles and focus during installation to minimize blind spots and glare from windows or lights.
Cable Management and Power
Organize cables using conduits, raceways, or cable trays to maintain neat installations. Label cables for easy identification and troubleshooting. Power over Ethernet simplifies installations by providing both data and power through a single cable, reducing the need for separate power supplies. For larger buildings, centralizing PoE switches in network closets per floor optimizes power distribution and simplifies maintenance.
Storage and RAID Configuration
Multi floor surveillance generates significant video data. Enterprise NVRs often support multiple hard drives with RAID configurations such as RAID 5 or 6 for redundancy and continuous operation. Calculate storage requirements based on the number of cameras, resolution, frame rate, and retention period. High capacity surveillance hard drives are recommended for reliability and 24×7 operation. Implementing RAID ensures that a drive failure does not compromise recorded footage.
Remote Access and Monitoring
Enable secure remote access for security personnel to monitor multiple floors from a centralized station or mobile devices. Use VPNs, secure P2P connections, or cloud enabled NVR features to allow remote monitoring without exposing the system to public internet risks. Assign user roles and permissions to control access to live feeds, playback, and system settings. Multi user access enables coordinated monitoring across floors and departments.
AI and Analytics Integration
Enterprise NVRs in multi floor buildings may include AI analytics for motion detection, people counting, facial recognition, or access control integration. Position cameras strategically to maximize AI effectiveness, and configure NVR analytics for each camera individually. AI can alert security staff to unauthorized access, suspicious behavior, or overcrowding in common areas. For large buildings, centralized AI processing reduces load on individual cameras and improves response times.
Testing and Calibration
After installation, test each camera and verify connectivity to the NVR. Check live streams, recording quality, motion detection, and AI analytics. Adjust camera angles, focus, and sensitivity as needed. Ensure remote access works for all authorized users. Conduct scenario testing such as simulating motion events, power interruptions, or network issues to validate system resilience and reliability. techners
Maintenance and Monitoring
Regular maintenance ensures long term performance. Check storage health, firmware updates, network performance, and camera functionality periodically. Clean camera lenses, inspect mounts, and monitor for physical or environmental damage. Enterprise NVRs provide logging and alerting features that help detect failures or anomalies early. Scheduled maintenance reduces downtime and preserves recorded video integrity.
Scalability and Future Proofing
Multi floor buildings often expand or change usage over time. Design the NVR system with scalability in mind, allowing additional cameras, storage, or AI features to be added without replacing the core system. Document network layouts, IP addresses, camera settings, and NVR configurations for easier expansion. Future proofing ensures the system adapts to changing building requirements or technological advancements.
Conclusion
Setting up an NVR for multi floor building surveillance requires comprehensive planning, careful network design, enterprise grade hardware selection, strategic camera placement, and ongoing maintenance. Enterprise NVRs provide scalability, storage, AI analytics, and robust performance to handle multiple cameras and high resolution streams. Proper installation, cable management, and secure remote access ensure reliable monitoring across all floors. By following best practices, installers and security managers can deploy efficient, high quality surveillance systems in commercial buildings, residential complexes, retail stores, and industrial facilities in 2025 and beyond.
Read more: https://enhanceyourwebsites.com/how-do-i-fix-nvr-overheating-issues-during-long-recording-hours/












Leave a Reply