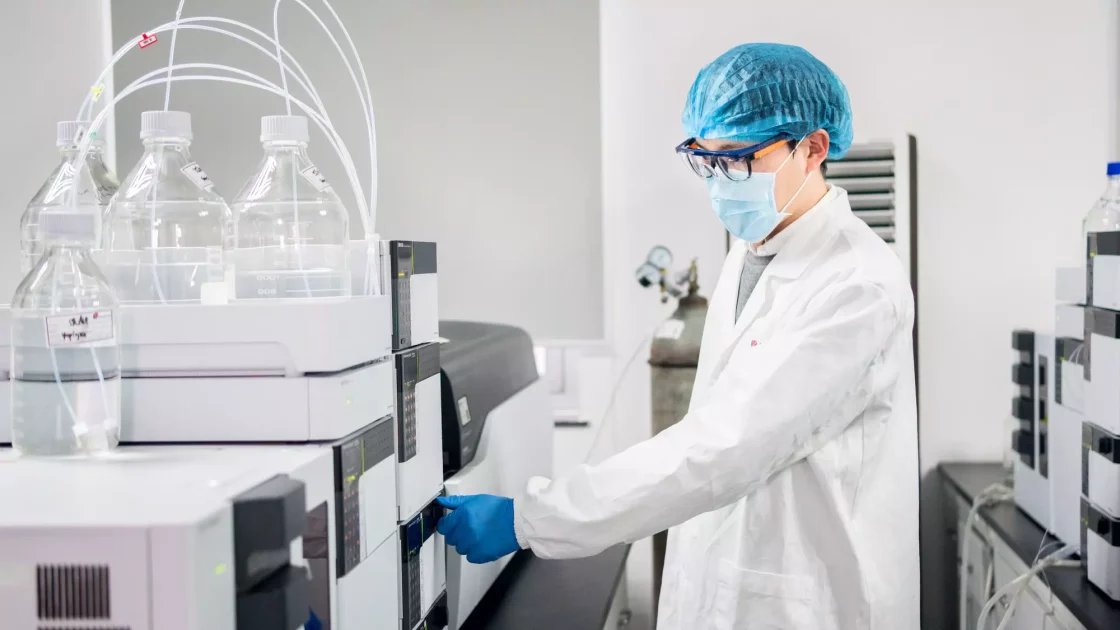
Accurate pharmacokinetic data is crucial for the success of drug development programs. Advanced analytical capabilities directly impact clinical trial outcomes, regulatory approval decisions, and therapeutic optimization initiatives. Pharmacokinetic (PK) labs are specialized facilities equipped with expertise and advanced instrumentation for conducting pharmacokinetic studies across all phases of discovery and development.
PK assay development is critical in generating precise data on drug concentrations, exposure characterization, and bioavailability assessment. Comprehensive Bioanalytical Services help pharmaceutical companies through expert analytical solutions necessary for successful regulatory submissions and pharmacokinetic clinical trials. This article dives into the capabilities, methodologies, and service offerings of PK Laboratories to support comprehensive pharmacokinetic programs.
Pharmacokinetics studies for large and small molecules
The bioanalytical aspect of PK studies is critical, and experts at PK labs understand these complexities revolving around PK methods and sample testing. These experts efficiently perform the bioanalytical aspect of PK studies at each stage of drug development.
Large molecule pharmacokinetic studies
PK Labs often performs large molecule bioanalysis using ligand-binding assays such as ECL or ELISA assays. The Meso Scale Discovery method has emerged as a popular tool for large molecule PK analysis. In some instances, experts at PK labs may employ hybrid LC-MS/MS methods to develop and validate approaches for mass spec assessments of large molecules. Large molecules and small molecules differ significantly, and hence their PK profiles are also different. The adsorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion largely differ between small and large molecules, affecting PK drug profiles.
Must Read: How to Choose the Right Bioanalysis Lab for Your Clinical Study?
Small molecule pharmacokinetic studies
PK labs generally perform small molecule bioanalysis using LC-MS/MS systems. Over the last decades, the sensitivity of LC-MS/MS assays has increased drastically, with most units detecting compounds and molecules in the picogram and nanogram levels. High sensitivity is essential for small molecule bioanalysis. Hence, sponsors should select a laboratory with high-end instruments capable of assessing drug concentrations in the desired range. PK labs use advanced mass spec instruments and technologies for robust PK analysis.
Pharmacokinetic method development
Drug developers should design and develop a bioanalytical method for drugs as soon as possible in the discovery and development process. Generally, PK studies are needed in the discovery and development phase to evaluate and identify lead compounds. Hence, choosing an advanced PK lab is critical as they are equipped with the necessary expertise to deliver rapid and accurate results.
Pharmacokinetic bioanalytical validation
The method employed in analytical studies advances as the drug candidate progresses towards clinical studies. Once PK labs begin GLP studies, the developed method for pharmacokinetic studies must be validated. Method validation is crucial for regulatory-compliant bioanalysis. GLP-compliant studies are not only needed by the US FDA, but they also ensure consistent, reliable, and accurate results. A fully validated bioanalytical assay is needed for all methods employed in clinical studies and pivotal nonclinical studies.
A full assay validation typically follows the FDA Guidance Document for Bioanalytical Method Validation, which needs testing for specificity, selectivity, calibration curve, matrix effects, accuracy, precision, range, linearity, reproducibility, and stability. Scientists at PK Labs routinely validate methods for multiple studies and experiments.
Discovery DMPK studies
The early approach to discovering DMPK bioanalysis is critical to evaluating lead compounds. After the preliminary screening of lead compounds in the discovery stage of drug development, thousands of compounds are available for testing. Drug developers have to identify the right candidates to transition them to the next stage. They characterize these lead compounds to evaluate their potential as a future drug product. One approach to narrow down on viable compounds is to perform drug metabolism and pharmacokinetic studies. Earlier, poor PK properties were one of the primary reasons for drug failure. By conducting early PK studies, drug developers can confidently identify molecules in the lead selection stage.
Preclinical pharmacokinetic studies
Preclinical pharmacokinetic assays determine the dose and safety of drug candidates before human trials. Preclinical PK studies conducted as part of IND applications must be GLP-compliant. Generally, preclinical PK studies for regulatory submissions are conducted in non-rodent and rodent species. The preclinical pharmacokinetic data are used to determine the human equivalent dose. A favorable PK data in preclinical assessment ensures the efficacy and safety of the drug candidate. A reliable PK lab will have expertise in performing PK studies in the preclinical stages.
Clinical PK studies
In clinical trials, the primary objective of PK studies is to identify the correct doses relevant to the patient populations. Phase I clinical trials focus on dose escalation studies consisting of single and multiple ascending dose assessments. Phases II and III consist of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic dose-response studies and pivotal bioequivalence assessments.
The road ahead for PK Labs
Specialized PK labs play an essential role in supporting pharmacokinetic studies and pharmaceutical development programs. Today, comprehensive bioanalytical services and expert PK assay development are necessary for generating reliable pharmacokinetic data. Besides, PK ELISA and PK LC-MS assays have enabled successful regulatory submissions and pharmacokinetics clinical trials. In conclusion, understanding the strategic potential of PK labs will be critical in enhancing therapeutic innovation and accelerating drug development timelines.














Leave a Reply