Introduction
Brain tumors are abnormal growths of cells within the brain that can disrupt normal brain function. They can be classified as either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and their effects depend on their size, location, and growth rate. While some brain tumors grow slowly and may not immediately impact health, others can be aggressive and life-threatening, making early detection and appropriate treatment crucial. This article explores the processes involved in diagnosing brain tumors, the available treatment options, and the latest advancements in the field.
Definition
Brain Tumor Diagnosis and Treatment refers to the medical process of identifying abnormal growths in the brain through techniques such as imaging scans, biopsies, and neurological examinations, followed by interventions to manage or remove the tumor. Treatment may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or a combination, depending on the tumor type, size, location, and the patient’s overall health, with the goal of reducing symptoms, controlling tumor growth, and improving quality of life.
Understanding Brain Tumors
Brain tumors originate from various types of cells in the brain or nearby structures. They are broadly categorized into primary and secondary (metastatic) tumors. Primary brain tumors originate in the brain itself, while secondary tumors spread from cancers located in other parts of the body, such as the lungs or breast. Common types of primary brain tumors include:
- Gliomas: Arise from glial cells and include astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and glioblastomas.
- Meningiomas: Develop in the meninges, the protective layers covering the brain.
- Pituitary adenomas: Affect the pituitary gland and can disrupt hormonal balance.
- Medulloblastomas: More common in children, originating in the cerebellum.
The symptoms of a brain tumor vary depending on the tumor’s location, size, and rate of growth. Some common symptoms include persistent headaches, nausea, seizures, vision or speech problems, balance issues, and cognitive or behavioral changes. However, these symptoms are not exclusive to brain tumors, making proper diagnostic evaluation essential.
Diagnosing Brain Tumors
Early and accurate diagnosis of a brain tumor significantly improves the chances of effective treatment. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history evaluation, neurological examination, imaging studies, and sometimes tissue biopsy.
Neurological Examination:
The initial step involves a detailed neurological exam to assess functions such as reflexes, coordination, muscle strength, vision, hearing, and cognitive abilities. Abnormalities detected during this exam can provide clues about the tumor’s location and impact on brain function.
Imaging Studies:
Imaging techniques are essential in detecting and evaluating brain tumors. The most commonly used imaging methods include:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI is the gold standard for brain tumor detection. It provides detailed images of brain structures, helping to determine the size, location, and extent of the tumor. Advanced MRI techniques, such as functional MRI (fMRI) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), can offer additional insights into tumor activity.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: CT scans are particularly useful in emergency situations or when MRI is unavailable. They provide a quick assessment of brain abnormalities and are effective in detecting bleeding or calcifications associated with tumors.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan: PET scans can help distinguish between benign and malignant tumors by measuring the metabolic activity of brain cells.
Biopsy:
A definitive diagnosis often requires a biopsy, where a small sample of tumor tissue is extracted and examined under a microscope. Biopsies can be performed using minimally invasive techniques like stereotactic needle biopsy or during surgical tumor removal. Pathological analysis helps identify the tumor type, grade, and potential genetic mutations, which guide treatment decisions.
Molecular and Genetic Testing:
Recent advancements in oncology have made molecular and genetic testing an essential part of brain tumor diagnosis. Tests can identify specific genetic mutations or molecular markers, allowing for personalized treatment approaches and better prognostic predictions.
Treatment Options for Brain Tumors
The treatment plan for a brain tumor depends on several factors, including tumor type, size, location, growth rate, and the patient’s overall health. A multidisciplinary approach involving neurosurgeons, oncologists, radiologists, and other specialists is often required.
1. Surgery
Surgery is typically the first-line treatment for accessible brain tumors. The primary goal is to remove as much of the tumor as safely possible without damaging surrounding healthy brain tissue. Surgical options include:
- Craniotomy: A procedure where a portion of the skull is removed to access and excise the tumor.
- Minimally invasive surgery: Techniques such as endoscopic surgery reduce trauma and accelerate recovery.
While surgery can significantly reduce tumor burden, complete removal may not always be possible, especially for tumors near critical brain regions.
2. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to destroy tumor cells or inhibit their growth. It is commonly used when surgical removal is not feasible, to target residual tumor cells post-surgery, or in combination with chemotherapy. Techniques include:
- External beam radiation therapy: Delivers precise radiation from outside the body.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS): A non-invasive, highly focused form of radiation, ideal for small or hard-to-reach tumors.
3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells or stop their growth. It can be administered orally or intravenously and is often combined with other treatments. Chemotherapy effectiveness depends on the tumor type and its sensitivity to specific drugs. Some commonly used drugs include temozolomide for glioblastomas and carmustine wafers for localized therapy.
4. Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
Advances in molecular biology have led to the development of targeted therapies that attack specific genetic mutations within tumor cells. Immunotherapy, which stimulates the body’s immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells, is also emerging as a promising treatment, especially for aggressive brain tumors.
5. Supportive and Palliative Care
In addition to curative treatments, supportive care is vital to manage symptoms such as headaches, seizures, and neurological deficits. Palliative care focuses on improving quality of life, particularly for patients with advanced or inoperable tumors.
Future Trends of Brain Tumor Diagnosis and Treatment Market
Advanced Imaging Technologies:
The market is expected to witness growth with the adoption of advanced imaging modalities like high-resolution MRI, PET-MRI fusion, and functional imaging, enabling earlier and more accurate diagnosis of brain tumors.
Personalized and Targeted Therapies:
Increasing focus on genetic profiling and molecular diagnostics is driving personalized treatment approaches, including targeted therapies and immunotherapy, tailored to individual patient profiles.
Minimally Invasive Procedures:
Surgical innovations, such as endoscopic and robotic-assisted neurosurgery, are improving patient outcomes by reducing complications, hospital stays, and recovery times.
AI and Machine Learning Integration:
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing diagnostics and treatment planning by enhancing tumor detection, grading, and predicting treatment responses.
Rising Investments and Collaborations:
Growing investments from pharmaceutical companies, biotech firms, and research institutions, along with global collaborations, are accelerating the development of innovative therapies and diagnostic solutions.
Growth Rate of Brain Tumor Diagnosis and Treatment Market
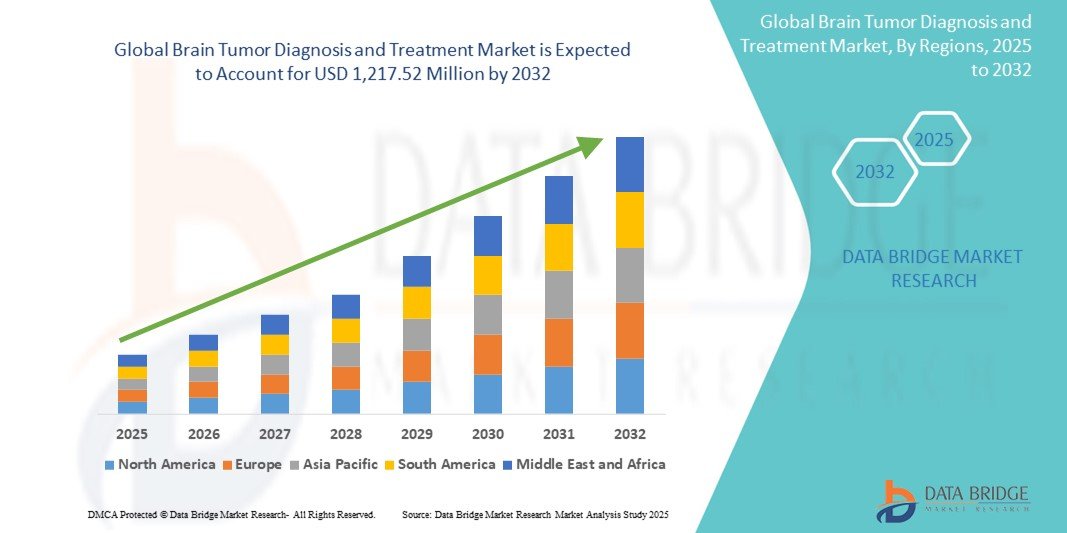
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the size of the global brain tumor diagnosis and treatment market was estimated at USD 666.62 million in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.82% to reach USD 1,217.52 million by 2032.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-brain-tumor-diagnosis-and-treatment-market
Conclusion
Brain tumors pose significant medical challenges due to their complexity and potential impact on neurological function. However, early diagnosis, precise imaging, biopsy analysis, and a combination of surgical, medical, and technological interventions provide hope for many patients. Ongoing research and innovative therapies continue to improve survival rates and quality of life, offering a more personalized approach to treatment.











Leave a Reply