Introduction
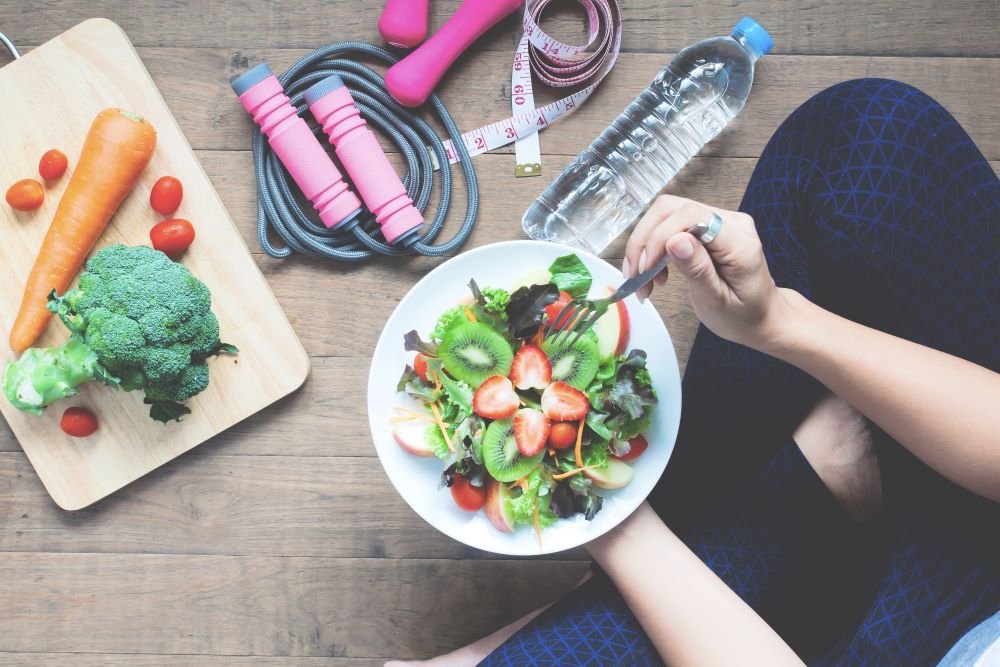
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions worldwide. While medications are commonly prescribed to manage blood sugar levels, diet and exercise play a fundamental role in controlling and even potentially reversing the condition. This article explores how lifestyle modifications, particularly proper nutrition and physical activity, can help individuals effectively manage type 2 diabetes.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough of it, leading to high blood sugar levels. If you are looking for type 2 diabetes treatment then you can also try Metformin hcl 500 mg from dose pharmacy to treat it. Unlike type 1 diabetes, which is an autoimmune condition, type 2 diabetes is largely influenced by lifestyle factors such as diet, physical activity, and obesity.
The Role of Diet in Managing Type 2 Diabetes
What you eat has a direct impact on blood sugar levels. A well-balanced diet can help regulate glucose levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and support overall health.
1. Emphasize Low-Glycemic Foods
The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly foods raise blood sugar. Low-GI foods, such as whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables, help maintain steady glucose levels.
2. Incorporate Fiber-Rich Foods
Fiber slows digestion, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar. Good sources include vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes.
3. Choose Healthy Carbohydrates
Opt for complex carbohydrates like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread instead of refined sugars and white flour products.
4. Increase Lean Proteins
Lean proteins, such as chicken, fish, tofu, and beans, help keep you full longer and stabilize blood sugar levels.
5. Healthy Fats Are Essential
Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil improve insulin sensitivity.
6. Limit Processed Foods and Sugary Beverages
Highly processed foods and sugary drinks lead to quick blood sugar spikes and contribute to insulin resistance.
Exercise and Type 2 Diabetes Management
Physical activity is just as important as diet in managing it. Regular exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, helping the body utilize glucose more efficiently.
1. Aerobic Exercise
Activities like walking, running, cycling, and swimming help lower blood sugar levels and improve heart health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
2. Strength Training
Building muscle improves insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Incorporate resistance training, such as weight lifting or bodyweight exercises, at least two times per week.
3. Flexibility and Balance Exercises
Yoga and stretching help reduce stress and improve overall mobility, which is beneficial for diabetes management.
4. Daily Movement Matters
Small changes, like taking the stairs, walking after meals, and standing instead of sitting for long periods, contribute to better blood sugar control.
The Synergy Between Diet and Exercise
Combining a healthy diet with regular exercise maximizes diabetes management benefits. A balanced meal before workouts prevents blood sugar fluctuations, while post-exercise nutrition supports recovery and glucose regulation.
Additional Lifestyle Factors for Diabetes Control
Beyond diet and exercise, other lifestyle factors play a role in diabetes management.
1. Prioritize Sleep
Poor sleep can increase insulin resistance and lead to weight gain. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
2. Manage Stress
Chronic stress triggers hormone imbalances that affect blood sugar levels. Mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation techniques can help.
3. Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water helps regulate glucose levels and supports kidney function.
While it is a lifelong condition, it can be effectively managed—and even reversed in some cases—through proper diet and exercise. Adopting a healthy lifestyle not only improves blood sugar control but also enhances overall well-being. By making conscious choices about food and staying active, individuals can take charge of their health and lead fulfilling lives despite diabetes.
FAQS
1. Can Type 2 Diabetes be reversed with diet and exercise?
Yes, in some cases, diet and exercise can help manage and even put it into remission. Losing weight, maintaining a balanced diet, and regular physical activity can significantly improve blood sugar control.
2. What foods should I eat to manage Type 2 Diabetes?
A diabetes-friendly diet includes whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, fiber-rich vegetables, and low-glycemic fruits. Avoid processed foods, added sugars, and refined carbs.
3. How much exercise is needed to manage Type 2 Diabetes?
Experts recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, combined with strength training exercises.
4. Can weight loss help with Type 2 Diabetes?
Yes, even losing 5-10% of body weight can improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar levels, making diabetes easier to manage.
5. What type of exercise is best for Type 2 Diabetes?
A combination of aerobic exercises (like brisk walking or swimming) and resistance training (such as weightlifting or yoga) is ideal for managing blood sugar levels.
6. Can I still eat carbs with Type 2 Diabetes?
Yes, but it’s essential to choose complex carbs like whole grains, legumes, and vegetables rather than refined carbs like white bread and sugary snacks.
7. How does exercise help with blood sugar control?
Exercise helps muscles use glucose more efficiently, lowers insulin resistance, and supports overall metabolic health.
8. Are there specific diets recommended for Type 2 Diabetes?
Diets like the Mediterranean diet, low-carb diet, and plant-based diet have shown positive effects in managing diabetes. Consulting a healthcare provider for personalized guidance is best.
9. What are the best snacks for Type 2 Diabetes?
Healthy snacks include nuts, Greek yogurt, hummus with veggies, boiled eggs, and low-sugar protein bars.
10. How long does it take for diet and exercise to show results in managing Type 2 Diabetes?
It varies from person to person, but noticeable improvements in blood sugar levels can occur within a few weeks of consistent healthy eating and exercise habits.









Leave a Reply