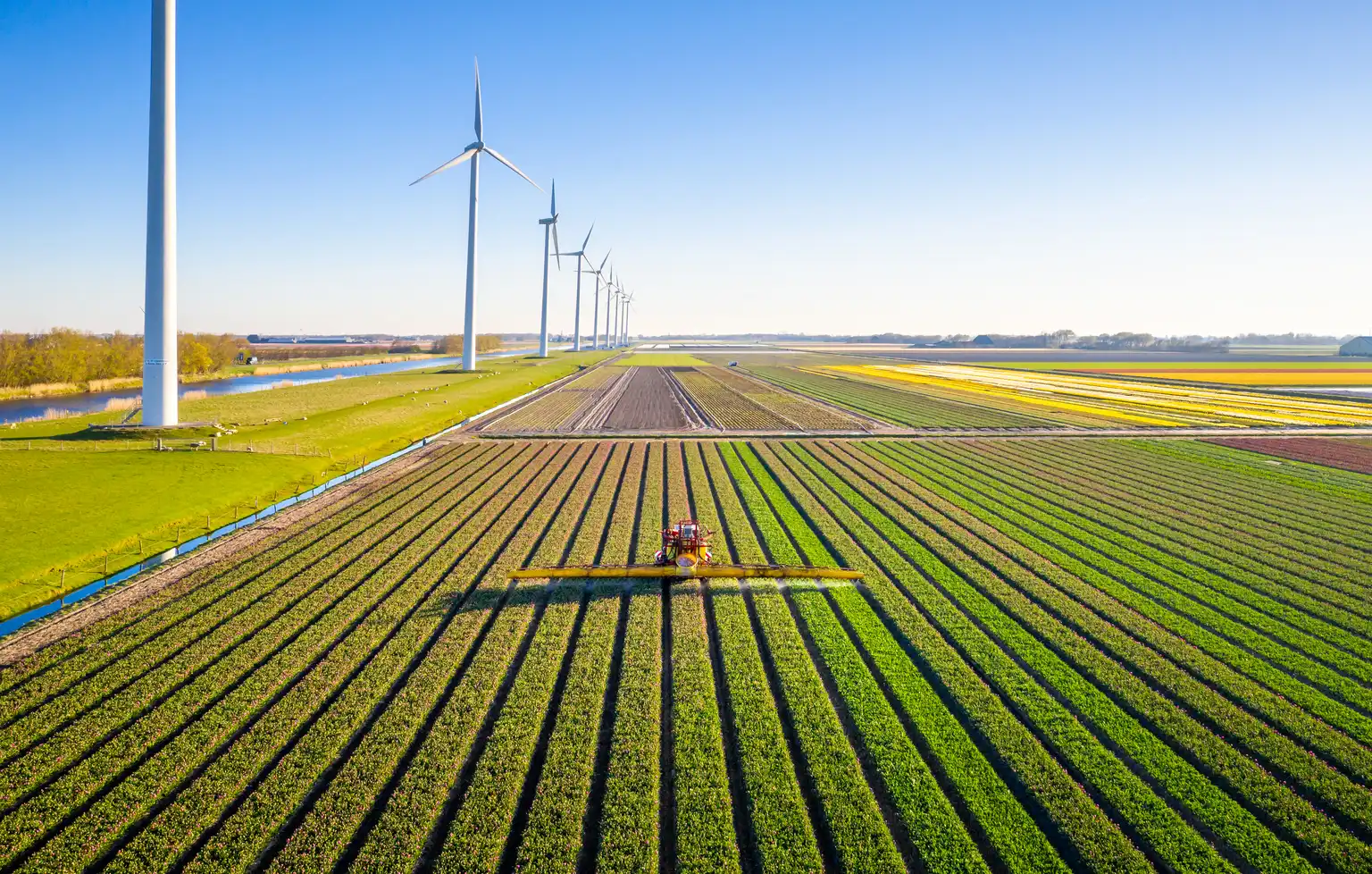
Have you ever wondered how your food gets from the farm to your plate—and what it costs the planet? That’s where sustainable agriculture comes in. It’s a farming approach that balances the need for food production with the need to care for the environment, support farmers, and maintain healthy communities.
Unlike conventional farming, which often focuses on short-term yields and heavy use of chemical inputs, sustainable agriculture looks at the bigger picture. It aims to preserve natural resources like soil, water, and biodiversity while ensuring farming remains viable for future generations.
In simple terms, it’s about growing food in a way that’s good for people, the planet, and profits. Whether you’re new to the concept or just want a refresher, this beginner-friendly guide will walk you through what sustainable agriculture means, why it’s important, and how it works in the real world.
What Does “Sustainable” Really Mean in Farming?
Sustainability in agriculture isn’t just about being “green.” It’s about farming that:
- Protects the environment (like preventing soil erosion and conserving water),
- Supports farm communities (fair wages, local markets, and farmer well-being), and
- Delivers long-term productivity (healthy soil = healthy crops for years to come).
A sustainable farm works with nature, not against it. It uses fewer harmful chemicals, recycles nutrients, conserves energy, and often integrates crops and livestock in smarter ways. It’s designed to be resilient—to bounce back from challenges like droughts, pests, and changing markets.
The 3 Pillars of Sustainable Agriculture
To keep it simple, sustainable agriculture is built on three main pillars:
1. Environmental Health
- Crop rotation, organic fertilizers, composting, and conservation practices protect natural ecosystems.
- Less pollution and more biodiversity lead to cleaner air, water, and soil.
2. Economic Profitability
- Sustainable farms aim for long-term profits, not just quick harvests.
- By reducing costs on chemicals and improving soil health, farmers often see better returns over time.
3. Social and Community Well-being
- Supporting rural communities through fair labor, local food systems, and education.
- Farmers aren’t just food producers—they’re caretakers of culture and community.
Common Practices in Sustainable Agriculture
Here are a few techniques commonly used in sustainable farming:
- Crop Rotation: Changing crops regularly to improve soil and control pests.
- Organic Fertilizers: Using compost or manure instead of synthetic chemicals.
- Cover Cropping: Planting crops that prevent soil erosion and boost nutrients.
- Drip Irrigation: Conserving water by delivering it directly to plant roots.
- Agroforestry: Combining trees and crops to create more diverse, resilient farms.
Each farm may use a different mix of practices depending on the climate, soil type, and local needs.
How Is Sustainable Agriculture Different from Organic Farming?
While they often overlap, sustainable and organic farming aren’t the same.
- Organic farming follows strict rules about chemical use and certifications.
- Sustainable farming focuses more broadly on long-term impact—environmental, social, and economic.
Some sustainable farms are organic. Others may use a few synthetic inputs but still follow eco-friendly and socially responsible practices.
Benefits of Sustainable Agriculture
Why is this so important? Here are just a few benefits:
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Healthier Soil | More nutrients and better crop yields |
| Cleaner Water | Fewer pollutants in rivers and lakes |
| Reduced Emissions | Less fossil fuel use = lower carbon footprint |
| Support for Communities | Stronger local economies and fairer wages |
| Food Security | More stable food supplies in uncertain times |
Challenges Facing Sustainable Farming
It’s not always easy. Farmers face:
- Higher upfront costs for equipment or training
- Lack of access to knowledge or resources
- Market pressure for low-cost, mass-produced food
- Climate unpredictability
But with growing awareness and support from consumers and governments, more farms are making the switch.
How Can You Support Sustainable Agriculture?
Even if you’re not a farmer, you play a role! Here’s how:
- Buy local or seasonal food
- Choose certified sustainable or organic products
- Support farmer’s markets and CSAs
- Reduce food waste at home
- Advocate for policies that support green farming
Every small action adds up to a more sustainable food system.
Final Thoughts: A Greener Future Starts Here
Sustainable agriculture is more than a farming trend—it’s a necessary step toward a healthier planet. It’s about feeding today’s population without compromising tomorrow’s resources.
At Friend of the Earth, we believe everyone—from farmers to consumers—can help make food production part of the solution to global challenges. Whether you’re planting your first tomato or choosing sustainably grown products, you’re joining a movement that respects the earth and all who live on it.Have you ever wondered how your food gets from the farm to your plate—and what it costs the planet? That’s where sustainable agriculture comes in. It’s a farming approach that balances the need for food production with the need to care for the environment, support farmers, and maintain healthy communities.
Unlike conventional farming, which often focuses on short-term yields and heavy use of chemical inputs, sustainable agriculture looks at the bigger picture. It aims to preserve natural resources like soil, water, and biodiversity while ensuring farming remains viable for future generations.
In simple terms, it’s about growing food in a way that’s good for people, the planet, and profits. Whether you’re new to the concept or just want a refresher, this beginner-friendly guide will walk you through what sustainable agriculture means, why it’s important, and how it works in the real world.
What Does “Sustainable” Really Mean in Farming?
Sustainability in agriculture isn’t just about being “green.” It’s about farming that:
- Protects the environment (like preventing soil erosion and conserving water),
- Supports farm communities (fair wages, local markets, and farmer well-being), and
- Delivers long-term productivity (healthy soil = healthy crops for years to come).
A sustainable farm works with nature, not against it. It uses fewer harmful chemicals, recycles nutrients, conserves energy, and often integrates crops and livestock in smarter ways. It’s designed to be resilient—to bounce back from challenges like droughts, pests, and changing markets.
The 3 Pillars of Sustainable Agriculture
To keep it simple, sustainable agriculture is built on three main pillars:
1. Environmental Health
- Crop rotation, organic fertilizers, composting, and conservation practices protect natural ecosystems.
- Less pollution and more biodiversity lead to cleaner air, water, and soil.
2. Economic Profitability
- Sustainable farms aim for long-term profits, not just quick harvests.
- By reducing costs on chemicals and improving soil health, farmers often see better returns over time.
3. Social and Community Well-being
- Supporting rural communities through fair labor, local food systems, and education.
- Farmers aren’t just food producers—they’re caretakers of culture and community.
Common Practices in Sustainable Agriculture
Here are a few techniques commonly used in sustainable farming:
- Crop Rotation: Changing crops regularly to improve soil and control pests.
- Organic Fertilizers: Using compost or manure instead of synthetic chemicals.
- Cover Cropping: Planting crops that prevent soil erosion and boost nutrients.
- Drip Irrigation: Conserving water by delivering it directly to plant roots.
- Agroforestry: Combining trees and crops to create more diverse, resilient farms.
Each farm may use a different mix of practices depending on the climate, soil type, and local needs.
How Is Sustainable Agriculture Different from Organic Farming?
While they often overlap, sustainable and organic farming aren’t the same.
- Organic farming follows strict rules about chemical use and certifications.
- Sustainable farming focuses more broadly on long-term impact—environmental, social, and economic.
Some sustainable farms are organic. Others may use a few synthetic inputs but still follow eco-friendly and socially responsible practices.
Benefits of Sustainable Agriculture
Why is this so important? Here are just a few benefits:
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Healthier Soil | More nutrients and better crop yields |
| Cleaner Water | Fewer pollutants in rivers and lakes |
| Reduced Emissions | Less fossil fuel use = lower carbon footprint |
| Support for Communities | Stronger local economies and fairer wages |
| Food Security | More stable food supplies in uncertain times |
Challenges Facing Sustainable Farming
It’s not always easy. Farmers face:
- Higher upfront costs for equipment or training
- Lack of access to knowledge or resources
- Market pressure for low-cost, mass-produced food
- Climate unpredictability
But with growing awareness and support from consumers and governments, more farms are making the switch.
How Can You Support Sustainable Agriculture?
Even if you’re not a farmer, you play a role! Here’s how:
- Buy local or seasonal food
- Choose certified sustainable or organic products
- Support farmer’s markets and CSAs
- Reduce food waste at home
- Advocate for policies that support green farming
Every small action adds up to a more sustainable food system.
Final Thoughts: A Greener Future Starts Here
Sustainable agriculture is more than a farming trend—it’s a necessary step toward a healthier planet. It’s about feeding today’s population without compromising tomorrow’s resources.
At Friend of the Earth, we believe everyone—from farmers to consumers—can help make food production part of the solution to global challenges. Whether you’re planting your first tomato or choosing sustainably grown products, you’re joining a movement that respects the earth and all who live on it.







Leave a Reply