Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and a variety of other symptoms. Despite being one of the most common causes of chronic pain, it remains widely misunderstood and is often difficult to diagnose. Affecting millions of people worldwide, It’s primarily impacts women but can also affect men and children. It can severely disrupt daily life, affecting both physical and emotional well-being.
What is Fibromyalgia?
Fibromyalgia is a syndrome, which means it is a collection of symptoms rather than a specific disease. The primary symptom is widespread pain across the body, but other symptoms like fatigue, sleep disturbances, and cognitive issues, commonly referred to as “fibro fog,” also characterize the condition. While the exact cause of fibromyalgia is still unclear, research suggests that the brain and nervous system may process pain differently, leading to an amplified pain response.
Symptoms
Fibromyalgia manifests differently in each person, but the core symptoms are generally consistent. Some of the most common signs include:
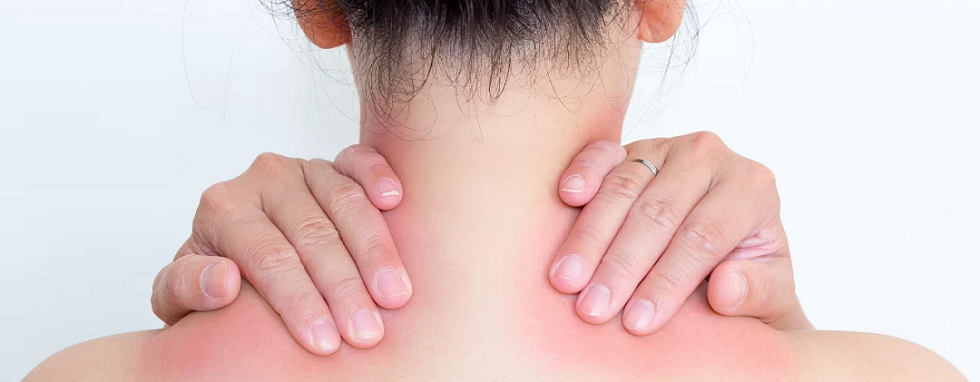
Widespread Pain: The hallmark symptom is pain throughout the body, often described as a deep ache, burning, or throbbing. The pain is typically located in the muscles, ligaments, and tendons, but it can affect any part of the body.
Fatigue: Chronic fatigue is another major symptom. Even with adequate rest, people with fibromyalgia often feel tired and lack energy.
Sleep Issues: Many individuals with fibromyalgia struggle with insomnia or disrupted sleep patterns. Restless leg syndrome and other sleep disorders are also common.
Cognitive Dysfunction: Often referred to as “fibro fog,” this includes difficulties with memory, concentration, and mental clarity.
Mood Disorders: Anxiety and depression are frequently reported in people with fibromyalgia, as the constant pain and lack of understanding from others can take an emotional toll.
Tender Points: These are specific areas on the body that are particularly sensitive to touch, such as the neck, shoulders, lower back, and hips.
What Causes Fibromyalgia?
While the exact cause remains uncertain, a number of factors are believed to contribute to the development of fibromyalgia. These include:
Abnormal Pain Processing: Research suggests that individuals with fibromyalgia have an abnormal response to pain signals. Their nervous system may amplify pain sensations, making the body more sensitive to stimuli.
Genetics: There appears to be a genetic component to fibromyalgia, as it often runs in families. Certain gene mutations may predispose individuals to developing the condition.
Infections and Trauma: Physical trauma, such as accidents or surgery, and infections, such as the flu, have been linked to triggering fibromyalgia in some individuals.
Stress: Chronic stress is another potential trigger for fibromyalgia. Prolonged exposure to stress can alter the body’s pain perception and may contribute to the development of the condition.
Hormonal Imbalances: Fibromyalgia is more common in women, and hormonal factors may play a role in the condition. Changes in estrogen levels or other hormonal fluctuations may contribute to its onset.
Diagnosing Fibromyalgia
Diagnosing fibromyalgia can be challenging because there is no definitive test for the condition. Doctors rely on a combination of methods to diagnose fibromyalgia, including:
- Medical History and Physical Exam: A healthcare provider will evaluate the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and perform a physical exam to rule out other conditions.
- Tender Point Test: The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) defines fibromyalgia using a tender point test, where pressure is applied to 18 specific points on the body. If the patient feels pain in at least 11 of these areas, fibromyalgia is suspected.
- Exclusion of Other Conditions: Since fibromyalgia shares symptoms with other conditions, blood tests and imaging studies may be used to rule out other possible causes of the pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or thyroid disorders.
Treatment
Although there is no cure for fibromyalgia, a combination of treatments and lifestyle changes can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. Below are some of the most effective management strategies:
Medications
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can provide temporary relief from pain.
- Antidepressants: Medications like duloxetine (Cymbalta) and milnacipran (Savella) are use to help manage both pain and the mood disorders often associated with fibromyalgia.
- Anti-seizure Drugs: Gabapentin and pregabalin are medications that can help reduce pain and improve sleep by affecting the way nerves send pain signals to the brain.
- Muscle Relaxants: These may help alleviate muscle spasms and promote better sleep, which is often disrupted in fibromyalgia patients. Try Prosoma 500mg best muscle relaxants
Lifestyle Changes
Exercise: While it may seem counterintuitive, regular exercise is one of the best ways to manage fibromyalgia. Low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, and yoga can improve strength, flexibility, and reduce pain. Exercise also helps release endorphins, which are natural mood elevators and pain relievers.
Sleep Hygiene: Since poor sleep is common in fibromyalgia patients, establishing a consistent sleep routine is essential. Relaxation techniques before bedtime, a dark and quiet sleep environment, and maintaining regular sleep hours can help improve the quality of rest.
Stress Management: Techniques like mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing, and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help manage the emotional and physical stress of fibromyalgia. Reducing stress can lessen symptom severity and improve overall well-being.
Balanced Diet: While there is no specific diet, eating a healthy, balanced diet can help support energy levels and general health. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and omega-3 fatty acids may reduce inflammation and support the body’s ability to cope with pain.
Alternative Therapies
Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. Many patients report pain relief and improved sleep with acupuncture treatments.
Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage can help reduce muscle tension, promote relaxation, and alleviate pain. It has been shown to be particularly effective for patients who experience muscle tightness.
Chiropractic Care: Chiropractic adjustments can help improve spinal alignment and reduce pain, though patients should consult with a healthcare provider before seeking this treatment.
Living with Fibromyalgia
Living with fibromyalgia can be challenging, but it is possible to manage the condition effectively with the right approach. A combination of medical treatment, self-care, and lifestyle changes can significantly improve symptoms and allow individuals to lead fulfilling lives.
Fibromyalgia can be a frustrating and isolating condition, but support groups and counseling can help individuals cope with the emotional and psychological challenges it brings.
Conclusion
Fibromyalgia is a complex and multifaceted condition that affects millions of people worldwide. With its diverse range of symptoms, including chronic pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and cognitive dysfunction, fibromyalgia can disrupt many aspects of daily life. However, by understanding the condition and adopting a comprehensive approach to management. Individuals can improve their quality of life and find relief from the symptoms.













Leave a Reply